Efficient learning of single copy quantum states
A quantum algorithm for state reconstruction
Quantum state tomography involves estimating a quantum state by repeatedly running the experiment, involving state preparation, evolution, and measurement, to estimate the output state, necessitating exponentially many state copies. In this peoject, we present an efficient algorithm to estimate with a small but non-zero probability of error $\epsilon$ the output state of the experiment.
The algorithm involves exponentiation of the given unknown state $\rho$ as follows:
\[\mathcal{V} = e^{i \rho \sqrt{\epsilon}}\]followed by the quantum phase estimation to get the eigenvalues of the given operator.
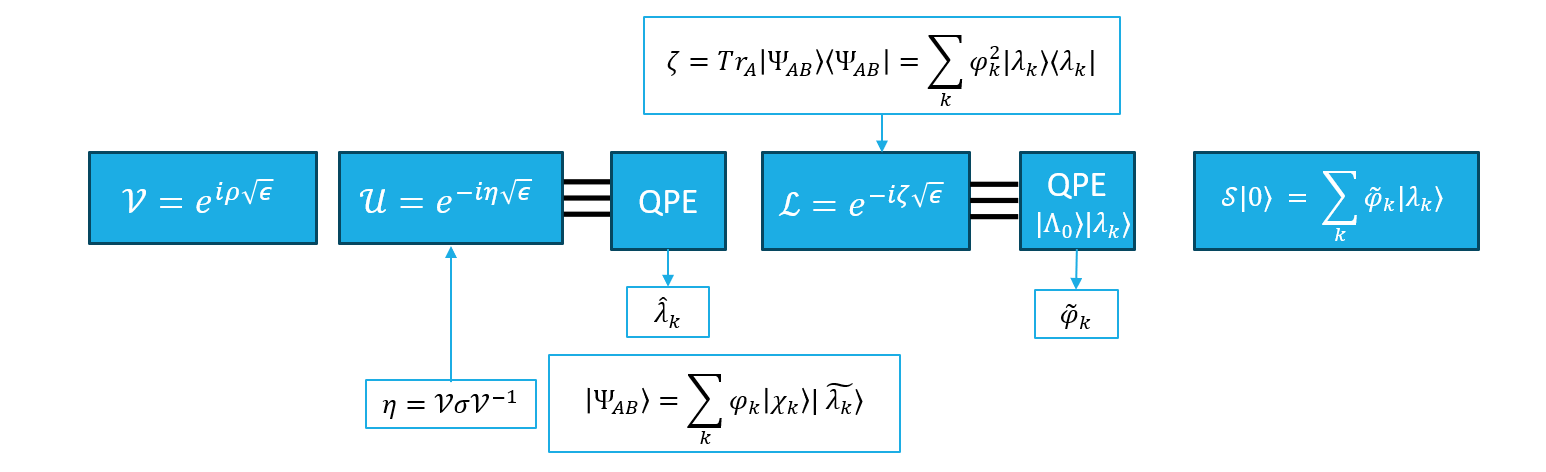
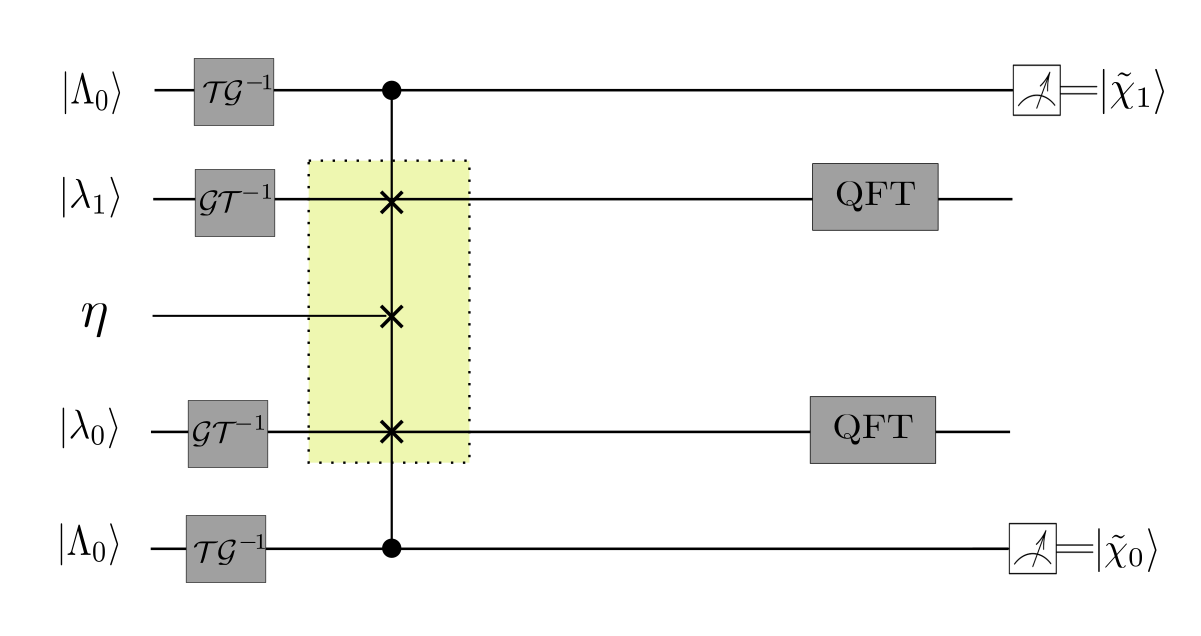
Further, as QPE requires $2^N$ evaluations for $2^N$ eigenvalues of a $N$ qubit system, we parallelized the QPE by usig SWAP operators to calculate all the phases at once.
To conclude, we presented an efficient quantum state tomography algorithm to estimate a quantum state with a single copy of the state, without knowing about the evolution dynamics of the state and without destroying the state. Quantum amplitude estimation for pure states, or quantum tomography for states, that can be mixed too, usually require many copies of the state, and so, as many runs of the experiment. By contrast, our method allows to efficiently estimate the $N × N$ density matrix of the state just after running the experiment once.